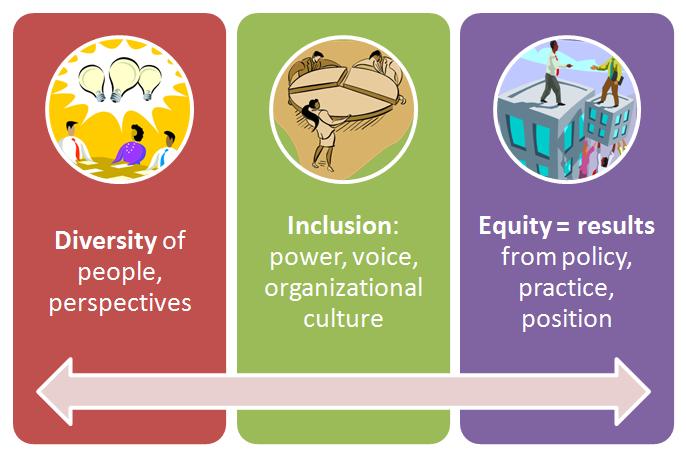
Posted in Power, Equity, Inclusion
April 4, 2018

The following is an excerpt from the third in a series of posts on networks, education and learning. The full post and series are published on the Education Week website. This post builds on two previous ones – Connection is Fundamental and Why Linking Matters – and looks at the importance of structure in supporting network effects while considering equity and power dynamics.
Networks are not necessarily easy to control in terms of their overall structure, especially when they are large and complex (diverse and widely distributed). And it is important to note that there are network phenomena that may tend to pull a networked endeavor in a certain structural direction.
For example, homophily is a phenomenon where social networks tend to form clusters of nodes with similar properties or attributes. This is captured by the adages, “Birds of a feather flock together,” and “Those close by form tight ties.” The result can be self-segregation along various lines of difference, for example racial, cultural, or class divisions in schools. Or consider the current pronounced political polarization in our country. The key to confronting homophily is to be both aware of the tendency and diligent about creating structures and incentives for bridging across boundaries.
“Opportunity … depends, at least in part, on our inherited networks.”
One of the great hopes and marvels of networks is that they can be liberating, especially in the face of bureaucracy and various barriers (see more about “network effects” in the previous post in this series). While this is worthy of celebration, another important phenomenon to be aware of is that networks can be deeply inequitable.
Read More
March 22, 2018
This post was originally published on this date in 2016 and we find it enduringly relevant today. It contains a true story and a Facilitator’s Guide for handling situations like this.
A True Story
At a recent training I was leading for an all queer and multiracial group, an older white man “John” took offense to my use of the word queer. As an icebreaker, I had asked the group to share in a pair, when did you first know you were queer? During the debrief, John took time to explain how the Q-word brought back painful memories of the many ways he was shamed growing up. As he explained, he got emotional and then said “using the Q-word is like using the N-word for me.” And he actually said the N-word.
The air in the room suddenly got heavy and many people shifted uncomfortably in their seats. The three black men in the group looked stunned, and the rest of the people of color in the circle turned to me to do something. The white man kept talking, completely unaware of that this micro-aggression had caused a change in the room. I waited for a white person to address what happened. But folks remained silent, so just as the next person began sharing, I stopped the process.
“I want to stop and check something out with you and the group. Is it ok if I do that?” I asked John and turned to the group to seek their approval. “John, thank you for sharing the impact that I had on you when I used the Q-word in this circle. I want to account to you for that. I also heard you use the N-word and I am wondering if you would be open to hearing the impact that that word could have had in the space?”
Read More
January 31, 2018

Power. Networks. Love. These three aspects of the IISC’s Collaborative Change Lens were not the official theme of the Victory Institute’s 2017 International Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender, and Queer (LGBTQ) Leaders Conference, but they were woven throughout everything that happened there.
The Victory Institute works to get LGBTQ people into elected and appointed office. Their annual conference brings together elected officials, leaders, and advocates for three-days. The content of the conference focuses on skill-building, information sharing, and formal and informal networking.
The first gathering of this group took place in 1984 with about a dozen people. Attendee John Heilman, city council member of West Hollywood, described the gathering as “more like a support group” than a conference. It has now grown to a convergence of over 500 attendees from all over the world.
Power
The reclaiming of power is central to the mission of the Victory Institute: “LGBTQ Victory Institute works to increase the number of LGBTQ people in public office and to provide programming, service and other support to help ensure their success.”
Why do we need more LGBTQ people in public office? With characteristic wit and bluntness, former U.S. Representative Barney Frank, the first person in Congress to come out voluntarily, said, “If you are not at the table, you are likely on the menu.”
The data tells the story this way: there is a direct correlation between the number of LGBTQs in elected office and the inclusion and equality of a jurisdiction’s policies.
Networks
In traditional ways, conferences tend to have a strengthening effect on networks. At plenaries and breakouts, attendees of the Victory conference had opportunities to connect around shared interests and maybe even to flirt a little. But the conference used the opportunity of the traditional schmoozing times to amplify traditionally marginalized voices. There was a “Leading in Color” reception which lifted up people of color, an International reception, and a Women Out to Win reception. The Institute also strengthened their pipeline for young leaders with the Victory Congressional Internship Meet & Greet.
Love
The feeling of love was palpable throughout the conference. Because of the bullying and harassment we’ve experienced, no one knows better than the LGBTQ community how much humans need to be celebrated and cheered. Whenever someone announced they were running for elected office, the audience burst into applause.
The spirit of love and humility was also present in a frequently repeated quote from Danika Roehm, the transgender metalhead stepmom, elected as the first openly transgender person to the Virginia Assembly – the first to serve in any state legislature actually. Roem won against Robert Marshall, the sponsor of a bill to restrict public bathroom use by transgender people, who referred to himself as Virginia’s “chief homophobe.” After the election, when asked if she had anything to say about Marshall, Roem said, “I don’t attack my constituents. Delegate Marshall is my constituent now.”
Pretty lucky constituent.
December 20, 2017

I’ve been observing the role of Mercury’s retrograde on my systems. Paying attention to my thoughts and feelings, the shifts and entrenchments. Lately I’ve been feeling a bit stuck. Or to use another metaphor, a bit ungrounded. It’s easy given the flow of information, the speed of communication, and the function of social media to feel pulled in many different directions. In addition, as a consultant, balancing the priorities of several clients at a time can often make it difficult to focus. When this happens I try to strengthen the consistency of my meditation practice and focus on my personal and professional goals to provide a guidepost for my actions.
I realized as I sat in meditation the past few mornings that my sense of purpose had been unattended to for a while. No wonder I felt scattered or ungrounded. Having a clear sense of purpose, an understanding of what I feel committed to and associated goals provides an important filter or straight line through all of the choices I face daily and helps to ground and retain focus. So I’ve been reflecting on purpose, leaning in to what is resonating for me in my conversations with colleagues and what is I am feeling called to in the movement. I’ve also been thinking about what threads together the work I am doing at IISC and my cultural work with Intelligent Mischief.
My commitment, or purpose, is to engage in transformation of myself and others towards liberation. This work aligns with what I do at IISC by supporting the self-empowerment of transformational leaders and by creating possibility for liberatory organizations that can really bring about the social transformation…that world, that speaks of, that “on a quiet day we can hear her breathing.” It also aligns with my work at Intelligent Mischief by cultivating a cultural shift that makes this transformation irresistible through the use of popular culture.
I reflected on what principles underscore this transformation for me…principles we can embody now at all levels to move us in the direction of liberation.
I see this transformation being underscored by a shift from isolation to interdependence, from exploitation to love, from extraction to regeneration & healing, from disconnection to community, from competition to collaboration, from exclusive ownership to the commons, from othering to belonging…and there are certainly many more.
These principles exist currently in practice but are overshadowed by the dominant culture especially at macro levels of society. Capitalism, our current dominant economic system, has been built on the principles that we are transitioning away from. The transformation of this system thus requires creating new systems based on the principles that we are transitioning towards. The question is, how do we expand these principles?
What can be our role at IISC in supporting leaders to develop practices that embody this transformation? In building structures that prefigure this transformation? And what is the transition in alignment with those principles that we ourselves must make as an organization?
December 11, 2017
“We must make just and liberated futures irresistible.”
Toni Cade Bambara (via Adrienne Maree Brown)
At IISC, we are asking ourselves what we are trying to accomplish by helping the ecosystem of organizations, networks, and leaders pursue racial equity. Are we clear what we are fighting for? I believe we need to imagine what a society without oppression would look like in order to be able to explore this question. If oppression were a thing of the past, what would the world be like? If white supremacy and the drive to dominate didn’t ravage our cultures and minds, what would be available to us?
At IISC, we talk about the “Fourth Box,” the box that remains after we have eliminated inequities and achieved human liberation. I believe equity will exist when enough people and structures in societies have successfully dismantled the tools and ideology of oppression. But what is the liberation that follows after the breakdown of oppression? The word “liberation” can get a funny reaction in some quarters because it sounds like a 1970’s throwback civil rights expression, but it’s a deeply important concept.
What if liberation is the personal and transformational freedom that comes when our society is no longer rigged for the few – those who share similar characteristics or benefit from systems to concentrate their power?
What if liberation instead created a society that is centered on the notion that all human beings naturally belong in this universe? A society in which people live with autonomy, resources, creativity, inspiration, love, and human connectivity that makes life joyful, meaningful, and in alignment?
If we were to be fully liberated, what would that look like? I believe we would simply have time for being human. We would naturally spend time with those around us, appreciating their gifts and uniqueness. We would create play, laughter, and art in the ways we did as children but with the knowledge and insights acquired from our adult experiences. We would bring to human beings around us the power of presence – the relaxed unrehearsed connectivity that brings forth love and harmonious existence with all things living. We would build a fortified earth that yields food, sun, beach, ocean, sky, moon, mountains, lakes, clouds, and a vibrant and healthy climate to all.
We will soon be spending time at IISC examining our racial justice approach and methodology. It is my hope that we will start from the premise of the world without oppression and then think about how we can best help our clients and networks discover what that looks like, feels like, tastes like, and sounds like. Let’s suspend time and give people the opportunity to imagine themselves free from oppression and the tools they were taught to dominate others so they can live into practices that transform our world.
What would it look like to design racial equity interventions by helping people envision the end of oppression?
November 29, 2017
Increasingly, social sector organizations are applying collaborative change frameworks and tools to engage in racial equity transformation. In a pattern reflective of the broader movement for racial justice, employees, often women of color in particular, are challenging organizational commitment to racial equity internally and programmatically. Often people who are ready to take action want to know what they can do to create space for the conversations needed to catalyze racial equity transformation.
The list of strategies below was generated by Marlon Williams, Ratna Gill, Madeline Burke and Kimberly Dumont, during our Fundamentals of Facilitation for Racial Justice Work workshop held in NYC earlier this month.
- Data: Use data to identify and initiate a conversation about inequities
- Training: Invest resources in training to staff to learn about racial equity and create the space for them to bring insights back to the organization
- Elevate Voices: Look for expertise throughout the organization’s hierarchy and give power to those with the capacity to lead, regardless of position.
- Personal Capital: Leadership and those with significant person capital can use if in service of prioritizing conversations about equity.
- Crisis: Incidents in the news that highlight the impact of our racial disparities can serve as a call to action.
- Personal Ownership: A commitment to racial equity should be owned by specific individuals throughout the organization’s structure.
- Outside Voices: Bring in outside voices to validate the need and urgency for having a focus on racial equity.
- Highlight the Loss: Identify the the risks or potential loss of not having a focus on racial equity.
Have you tried any of these strategies? Is your organization embarking on a journey of racial equity transformation? We can help.
November 20, 2017
“We know that there is no help for us but from one another, that no hand will save us if we do not reach out our hand.”
– URSULA K. Le GUIN

Image by Stephen Bowler, shared under provisions of Creative Commons Attribution license 2.0.
A note on the quotes below (and the Le Guin quote above): I am grateful for the beautiful piece by Evan Bissel, “Frames for Life, Liberation and Belonging,” which appears in the Othering and Belonging Journal. This piece lifts up some central elements of an emerging and humanizing narrative for our times, with focus on themes such as transition, liberation, belonging, commons, interconnection, abundance, sacred, curiosity, play, and place. I strongly encourage readers to check it out, to sit with the piece and let it soak in, and to share it.
This post follows the thread of a conversation that has been evolving across events I have been involved with the past few months, and a bigger and broader conversation that is clearly informing it. This is certainly not a new conversation, but there seems to be a renewed or perhaps more public vigor to it, at least in multi-racial and multi-generational social change groups and initiatives with which I have been involved.
It has cropped up in a network leadership program where a discussion about the difference between working for equity and working for justice pointed in the direction of the need to pursue liberation, and not simply inclusion and accommodation in fundamentally harmful systems. Read More
August 2, 2017

Photo credit: Ginko biloba leaves by James Field (Jame). Ginko trees are considered endangered even though they are cultivated worldwide, because so few live in the wild. This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unportedlicense.
I’ve often said that language is difficult, but it’s all (or at least most) of what we have to communicate complex ideas. I can remember when doing “diversity work” was seen as cutting edge, relevant, and powerful. It was an effort to change historic structures of exclusion, to change outcomes for people of color and women who suffered the brunt of racism and sexism. It was a chance to speak truth to power, and it seemed for a while that power was listening. Until it wasn’t. Or, more precisely, until the listeners started to hear “diversity” and think only about “heterogeneity.” With the stroke of a pen checking off boxes, the work was domesticated, watered down, simplified, and downsized into simply getting different faces in the place. And folks who were thinking bigger thoughts had to find new ways to talk and to get others to think and act on inclusion and equity.
I remember in the mid-2000s when I started saying “We don’t do diversity work, but if you want to think about diversity, equity, and inclusion, we might be the right people for you.” Now, I’m afraid, that equity might be running its course. I’m encouraged, on the one hand, by how many more people and organizations are asking questions about equity. And about how the equity conversation focuses on what we want, not what we don’t want. I’m all about the positive vision of life chances fulfilled without barriers based on any aspect of identity. And it’s also clear to me that some of those folks are using the language of equity precisely to avoid talking about racism, sexism, and other -isms that produce and sustain inequities. Somehow “equity” and even “inequities” are more comfortable rolling off the tongue than racism, classism, sexism, or homophobia. I wonder if “equity” as a concept is headed the way of “diversity.”
Still, if we are going to advocate for equity as the superior growth model for our country, as our friends from PolicyLink have so aptly argued, I wonder what language will help to keep our attention focused on dismantling the drivers of inequity in order to increase the odds that we’ll actually achieve something approaching equity. The science surrounding the origins, consequences, and remedies for unconscious bias or implicit association seem to be promising entry points for some people who are reluctant to enter a discussion doorway marked “racism” or “privilege.” And, research and practice around communications and messaging gives us other avenues to pursue. In these days of particularly fraught racial discourse, what are you finding useful in your practice? What are you finding gets in the way?
July 11, 2017
“Mutual learning is only possible when all participants are willing to be wrong … willing to learn, to explore new ideas, to go off the map, out of the known, and together grope in the shadowy corners of new ideas, new plans, new territories.”
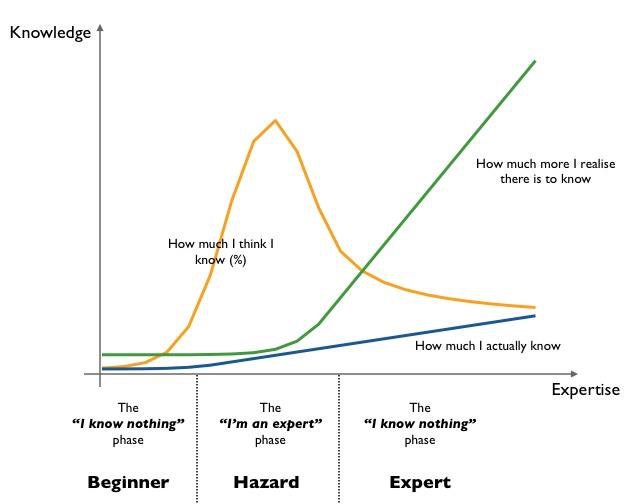
“Expertise” is one of those concepts that seems to get a good vetting every now and then, and in the current climate of VUCA (volatility, uncertainty, complexity, ambiguity) and networked approaches to change, there is certainly good reason for this. Mark Twain once quipped that what made the expert an expert was being from someplace else. There may be some truth and value to this view; when a set of “outside” eyes can lend fresh new perspective to a situation. And it is also the case that deference is often given to this version of expertise at the expense of local and other diverse sources of knowledge. Read More
June 13, 2017
“Life moves toward other life… If we trusted more in these cohering motions, we could move into an essential role … supporting the system to explore new connections, new information, new ways of being. It means focusing on opening the system in all ways.”
Margaret Wheatley and Myron Kellner-Rogers, a simpler way
“Bridging” in the work of network development speaks to the act of creating connections between socially heterogeneous groups (or putting it a bit more crassly, building bridges between “us” and “them”). The benefits of bridging include making it possible for diverse groups to share and exchange information, creating new forms of access, as well as leveraging new ideas and spurring innovation between groups representing different interests and/or backgrounds. Bridging widens social capital by increasing the “radius of trust.” Unlike “bonding,” or more in-group relationship building (think “birds of a feather flocking together”), bridging can help create more inclusive structures that can have implications for long-term resilience and more equitable development. The following is a story of a network engaging in intentional bridging work for more robust connectivity, flows and opportunity …
Food Solutions New England (FSNE) is a regional, collaborative network organized to “support the emergence of a New England food system that is a resilient driver of racial equity and food justice, sustainable farming and fishing, and thriving communities.” FSNE is convened by For the past 5+ years, IISC has worked with the convening “backbone organization,” UNH Sustainability Institute, to launch and structure itself as a formal network, as well as to concretize and evolve its core commitment to racial equity as it has become more diverse and inclusive and worked for systemic change.
Eighteen months ago, FSNE was faced with making a decision about where to hold its annual Food Summit. The Summit was originally conceived to bring together delegates from across New England to strengthen collaboration for regional food system sustainability. The commitment was made early on by the convenor to move the Summit around the region, holding it in each of the six New England states once before going to any of them for a second time.

Delegates to the 2015 New England Food Summit gathered in Boston, MA.
In 2016, Connecticut was the last state to host the New England Food Summit. The network’s backbone organization was faced with a decision about the specific location within the state. Previous Summits had been held in prominent hubs in the other states – Portsmouth (NH), Burlington (VT), Portland (ME), Pawtucket/Providence (RI) and Boston. While places like Hartford and New Haven might have been natural considerations given their respective amenities and relative centrality in the state, the choice was made to bring the Summit to Bridgeport. This decision was spurred in no small part by the leadership of State Senator Marilyn Moore, who hails from that city and is a member of the FSNE Network Team. Senator Moore pointed out that not only would it be significant for Bridgeport to play host, given it is often overlooked in favor of its more well-known and regarded neighbors, it would also be enlightening for Summit delegates to see reality on the ground. Furthermore, this choice was viewed as an expression of FSNE’s commitment to racial equity and food justice.
Read More
June 7, 2017
A couple of weeks ago, IISC was invited to offer a post-conference session at the Collective Impact Forum Conference in Boston. The title of this 8 hour session spread over two days was “Advancing Racial Justice Through and Within Collective Impact.” This was an opportunity for Cynthia Silva Parker and Curtis Ogden to formalize our ongoing efforts to bring IISC’s core collaborative methods, frameworks and a variety of racial justice content and tools to the different elements of the Collective Impact framework.
We were heartened to see and hear the many conversations about racial equity during the main conference proceedings, and noted good and challenging questions and exploration about the fit between the Collective Impact model, such as it has been formally presented and understood, and community organizing and power building work. These conversations continued in some form or fashion during our session. Read More
May 29, 2017
I recently received an email from the NorthSky Nonprofit Network about a practice group they have called the “Network Sandbox.” They introduce a tool (for “Tuesday Tool Time”) and invite members to play with it. I was happy to be told that they recently incorporated “connection stories” as a tool. Here is their invitation to participants to stretch and innovate:
This week’s tool is inspired by the new connections catalyzed by the mini-grants. While the survey we used collected some anecdotal information about the new connections, it left all of us wanting more… richer, deeper stories about these connections. Curtis Ogden from the Interaction Institute for Social Change (IISC), calls connection stories “critical nutrients” for networks that “feed a network forward.”
Tool: Connection Stories
Source: Interaction Institute for Social Change
Purpose: Collect and share stories of connections that have happened because of networks and share them back to the network to inspire more of the same.
From Curtis’s blog: Making these stories more explicit and accessible can have a number of different impacts:
- They model the importance of reaching out across boundaries and to “the other”
- They encourage network behaviors that build a foundation of trust and understanding, which …
- Contribute to “network effects” such as resilience, adaptation, and innovation.
- They can encourage cultures of equity, inclusion and diversity.