Not Just “Right Foods,” Right Access
More than 15 years ago I began educating women about breast cancer mortality and early detection. Most of my outreach centered around African American women who suffer the highest mortality even though the incidence is higher in white women than black women.
As a lay person, I find that what I don’t know allows me to look at issues from a common sense approach and ask those dumb questions. If every woman gets screened early why are their outcomes so bad? Sometimes the reason is the state of their health and when it is poor, they have poorer outcomes.
After educating over 15,000 women and witnessing first-hand how much they suffer through cancer and sometimes die, I learned that many of their outcomes were poor due to their overall general health. African Americans suffer from high rates of diabetes, heart disease, and cancer. Some of these women are battling more than one disease at a time. When a friend, who had her first chemo treatment, died at age 42 from a heart attack, I learned she was also diabetic and her diet lacked fresh fruits and vegetables.
We are surrounded by food deserts, the bodegas where most inner city people without transportation shop, don’t offer many healthy choices. Fresh fish, vegetables, and fruits are not available, cost prohibitive, and in the corner stores, unattractive. Urban communities need more local, affordable, and culturally appropriate foods.
As we look towards producing 50% of our food in the New England states by 2060 we must be mindful that if we are going to be inclusive, we must consider those who suffer the greatest health disparities. It’s not only about the right foods being available, but that we all have access.

Abundance Thinking for Change
About 20 years ago I was introduced to the field of ecological design called permaculture, not in any great depth mind you, but from what I learned at the time, I was struck by how refreshing, sensible, and vital the practitioners’ perspective and approach were. Since then, and especially in recent years, interest in permaculture seems to have significantly grown (including my own) and its principles stretched beyond sustainable agriculture to human communities. Looby MacNamara is one of the teachers and practitioners who is helping with the more widespread application of permaculture principles. I just finished reading her short book, 7 Ways to Think Differently, which I recommend. In it she unites different ways of thinking (such as systems thinking and solutions thinking) with the underlying philosophical and methodological elements of “regenerative design.”
For me, one particularly fertile area is “abundance thinking.” I have to offer a bit of a pre-qualification that the word “abundance” can be used in certain contexts that I find off-putting, especially when there is little demonstrated understanding of existing structural inequities in society. That said, I think that “leading with abundance” as a mental exercise can provide valuable insights and approaches to social change. Here are a few thoughts, and I invite additions, reactions and push back: Read More
4 Comments“What’s most systemic is personal”
“What’s most systemic is personal . . . and interpersonal.”
– rift on a Peter Senge quote
At IISC, one of the three core lenses that we bring to our collaborative capacity building for social change work is love as a force for social transformation. How this lens impacts what we do as practitioners depends on context, though often it comes down to ensuring that there is time for people in the collaborative change efforts we support to connect on a personal and interpersonal level. One way to do this is to invite people to share stories and do this beyond the parameters for their professionally defined roles. I did this recently with a group and as is often the case, there were a few areas of resistance in the collective body. “Why are we doing this?” asked someone with a hint of consternation. That became my opening. Here is what I offer as a response to discomfort around what some people call “touchy feely” exercises.
Why are we doing this?
- In general terms, to expand collective potential.
- To help each of us to be more fully seen and appreciated for who we are, beyond abstractions and implicit assumptions. When people do not feel seen or appreciated they can disengage, or “act out” to get the attention they want.
- To deepen connection, build trust and increase social velocity.
- To test and stretch the boundaries of “appropriate” and “legitimate” ways of knowing and being with one another. Otherwise people can default to ways that privilege those most comfortable with certain ways of being (often strictly professional and cerebral).
- To grow “positivity” – that is, to expand the overall collectively felt sense of positive emotions (which includes pride related to the demonstrated ability to have and hold difficult conversations). Positivity has been scientifically linked with greater physical and psychological capacity to see and take in more (of systems and one another).
I offer these, like a yoga teacher, with compassion for any expressed discomfort or tightness felt in different parts of the collective body. And the invitation is to breathe through this and to see what might be loosened up for the benefit of the whole. For another take on this, I highly recommend my friend Joe Hsueh’s piece “Why the Human Touch is Key to Unlocking Systems Change.”
Curious to hear your own experiences connecting what is most personal and interpersonal with systemic change.
1 CommentCreating Equitable Abundance
“We need to reach out to one another from a perspective that makes group membership less determinative of opportunity and more related to enhancement of self and community. We need to increase our sense of abundance and improve our sense of well-being, as individuals and in relation to one another. “
– john a. powell, Racing to Justice
I’ve had a number of conversations lately about mindsets and how they relate to effective collective and net work, especially work for justice. Most recently I had the opportunity to talk to Jim Ritchie-Dunham of the Institute for Strategic Clarity about his research into “thriving” organizations and communities in a number of diverse settings – sectors and countries. What he has noted as a shared and distinct (though surely not entirely sufficient) difference-maker for these groups is an orientation towards abundance.
Jim has recently published a book entitled Ecosynomics, which is also the name of a field he has helped to found, which looks at “the principles of collaboration” and more specifically, “the principles of abundance.” Research from Jim and his colleagues shows that even amidst what may appear to be a scarcity of resources and hope, some groups thrive in large part through the conscious construction of “agreements” that can create more opportunity.
I have questions and look forward to further conversation with Jim about the starting point of these groups and the degree to which dynamics of power and privilege come into play with respect to their respective successes and who ultimately benefits. At the same time, I have been aware in my work how much of a difference it can make for groups to be conscious of their ability to choose how to be with one another, and how this can help get beyond otherwise self- and collective-limiting behavior. Read More
1 CommentNetwork Development: Reflection is Key
It probably goes without saying that learning requires reflection. This holds true for individuals and groups, and yet what I find is that many collaborative efforts can fail to build adequate reflection time into their work. Often it seems that reflection can be cast aside in favor of “getting stuff done” and because, “There is so much to do!” And ironically, what can ensue is an overall and ongoing sense of impatience and frustration that “we aren’t doing anything or enough.” Experience shows that when people in networks and collaborative change work do pause to reflect, there is much value to be gained.
The other day I worked with the core team of a regional network focused on food system change, and we took time to reflect on what the past couple of years of work have yielded at individual, collective and systemic levels. People offered up their own reflections, as well as those garnered from informal interviews with others in the network. The result was eye-opening, affirming and provided a collective boost. What we agreed is that considerable and important development has occurred over time, including: Read More
2 CommentsFreedom and Unity: VTF2P Network Turns 4
“Our success is built on partnership, sharing success and sharing credit.”
– Sec. Chuck Ross

“The mojo is in the motto.” With these words, Secretary of Agriculture Chuck Ross opened the doors and conversation on the fourth annual Vermont Farm to Plate Network convening last Thursday in Killington. Each of the past four years Secretary Ross has brought some critical words of encouragement and motivation to this fall convening, and by invoking the state motto – “Freedom and Unity” – at this year’s opening he seemed to hit the right chords at a critical moment in the evolution of the network.
In 2011, Farm to Plate launched to great excitement and some anxiety as it positioned itself as a cross-sector collaborative network to carry out a strategic plan to double local food production in Vermont in 10 years time, contributing to job and economic growth as well as food access in a state that sees high rates of poverty. Since then, as both Ellen Kahler of the Vermont Sustainable Jobs Fund (the backbone organization for Farm to Plate) observed and remarked through a plenary retrospective, it has managed to find its collaborative footing and grow significantly in numbers (more than 300 organizations strong). And importantly, it has seen real results in terms of direct, indirect and induced job growth resulting in 9,000 new jobs in the agricultural and food sector in Vermont. Furthermore, success is evident in individual members using network goals to inform and align their organizational goals. Read More
1 CommentWhat is Network Strategy?
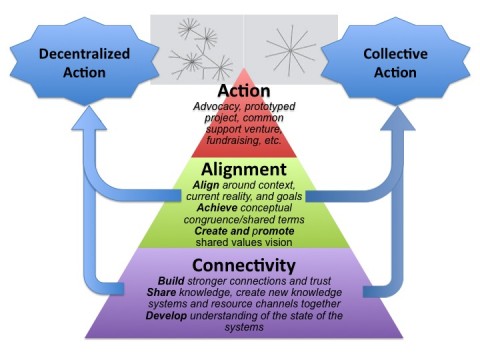 The above graphic is something that I recently created, borrowing heavily from the good work of Peter Plastrik and Madeleine Taylor, to help convey what is meant by engaging in “network strategy.” One of the challenges we’ve encountered in working with different networks is helping people to understand the difference between strategy development and network development. I try to meet this challenge, in part, by showing how they are not so different, or at least, that they are intimately connected. The diagram is also designed to help people get beyond some of the either/or thinking that we encounter. For example, it’s not that we have to choose between decentralized self-organized action and more formally coordinated collective action. It can be both!
The above graphic is something that I recently created, borrowing heavily from the good work of Peter Plastrik and Madeleine Taylor, to help convey what is meant by engaging in “network strategy.” One of the challenges we’ve encountered in working with different networks is helping people to understand the difference between strategy development and network development. I try to meet this challenge, in part, by showing how they are not so different, or at least, that they are intimately connected. The diagram is also designed to help people get beyond some of the either/or thinking that we encounter. For example, it’s not that we have to choose between decentralized self-organized action and more formally coordinated collective action. It can be both!
So here’s what the graphic is meant to convey. First of all, network strategy is grounded at a fundamental level in creating (strategic) connectivity, by building linkages and trust between key stakeholders and perhaps unusual bedfellows. This can be done by convening people; sharing stories, data and other forms of information; co-creating knowledge; learning together, etc. Part of the value of this connectivity is that it can lead to orthogonal thinking and bolster individual network participants’ efforts in the shared domain where the network is focused. What also may ensue is self-organized action between those who are meeting one another for the first time or getting to know one another better (see the arrow to the left side of the triangle). This is all well and good and is something that networks should try to track. Read More
Leave a commentWhy Equitable Networks?
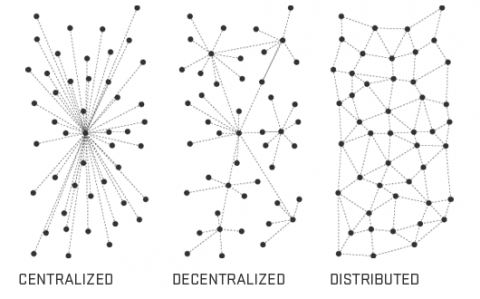
Readers of this blog know how much promise we at IISC see in networks to bring about greater depth and breadth of change in our country and communities. At the same time, we do not see networks as a panacea. In fact, there are good reasons to be vigilant about “net work” to ensure that it does not exacerbate the very conditions we are trying to remedy, especially when it comes to social inequities.
We have previously referenced the report from the Aspen Institute, The Power Curve Society, which considers the broad implications of a globally networked economy that allows greater ease of transactions. In this technologically accelerated economy, the report states, wealth increasingly and problematically concentrates in the hands of a few rather than spreading itself out across the larger population. This seems to be a natural emergent phenomenon of not just the unchecked networked economy but of many networks. As Kim Taipale notes, this is a paradoxical result of “network effects,” –
“Freedom results in inequality. That is, the more freedom there is in a system, the more unequal the outcomes become.”
This is because of something known as the “power-law distribution” that takes hold on open platforms, as wealth flows to the “super-nodes,” a phenomenon sometimes called “preferential attachment.” Read More
Leave a commentNetworks, Sensing and Surface Area
In recent work with a couple of different leadership development programs, I shared a few stories about organizations that failed to recognize the value of informal networks within and beyond their formal boundaries by choosing to see themselves primarily through the lens of the “org chart” and fixed roles/job descriptions (what I sometimes call the “stay in your lane” approach). In these cases what was lost was the ability to access greater organizational potential and intelligence. If we think of organizations as living entities, then our connections within and beyond those cellular walls might be thought of as vital nerves or sensors. When we fail to acknowledge or even cut these connections within, which often represent the pathways through which work actually gets done, we may stymie or destroy critical flows and functioning. And when we fail to see and leverage how people in all roles are connected beyond the organization, then we reduce not only the potential contribution of each individual, but the overall surface area of the organization that might otherwise attune it and help it to respond to larger systemic opportunities or threats. Which is why increasingly people are seeing mechanistic and fixed organizational roles as “irresponsible” – they do not allow people, individually and collectively, to effectively respond to circumstances and activate around that about which they care most. So the invitation is to think and act more like a living network. What are you doing to build greater sensitivity and surface area in your organization or change effort?
1 CommentHow Networks Can Change Systems
At this point a couple of networks with which I am working have reached or are reaching the three year mark in their formalized existence. By many accounts, this is a milestone and inflection point worth noting, as these initiatives have built significant connectivity (depth and breadth) and alignment (shared sense of common identity and direction) among key and diverse actors. Furthermore, there has been a real proven capacity of these networks to meet individual self/ organizational interests in terms of learning, new partnerships, and a broader community/marketplace of support. And there is a growing appetite for and interest in how this all adds up to significant system change. Another way of framing this is people are wondering how they can activate the next level of the system to bring all of their interactions to a place where there is greater abundance, opportunity, and impact. Read More
Leave a commentPoetry for Collective Impact
I have a practice in most of the networks and collective impact efforts I support, which is to offer poetry at the opening and closing of convenings. I’m struck by how impactful and important people have said this can be for them. In fact, just recently a very well-respected member of the public health community was compelled to say that this is exactly what is missing from the movement, more poetry and artistic expression!
1 Comment“Poems come out of wonder, not out of knowing.”
-Lucille Clifton
The “Right” Network Form?

Photo by Jenny Downing
Every now and then we get the question about what is the best way to structure a social change network, to which the most frequent response is, “It depends.” Case in point, in a past post, I offered examples of three different network forms growing out of the same region (New England) in a similar field (food systems). These forms that have evolved in three states have largely depended upon the initial framing question for the change effort (how to tackle food insecurity vs. how to grow the agricultural economy vs. how to achieve food justice), contextual factors (political dynamics, what already exists, who is engaged), and resources (not just funding, but certainly funding) available. And since the writing of that post, each has evolved, more or less significantly, in line with new challenges and opportunities. Some of the take-aways from this align with the lessons of moving from a more mechanistic to a regenerative outlook –
- start where you are with what actually is,
- avoid buying into “best practices,” and
- expect and even desire it to change as you go.






